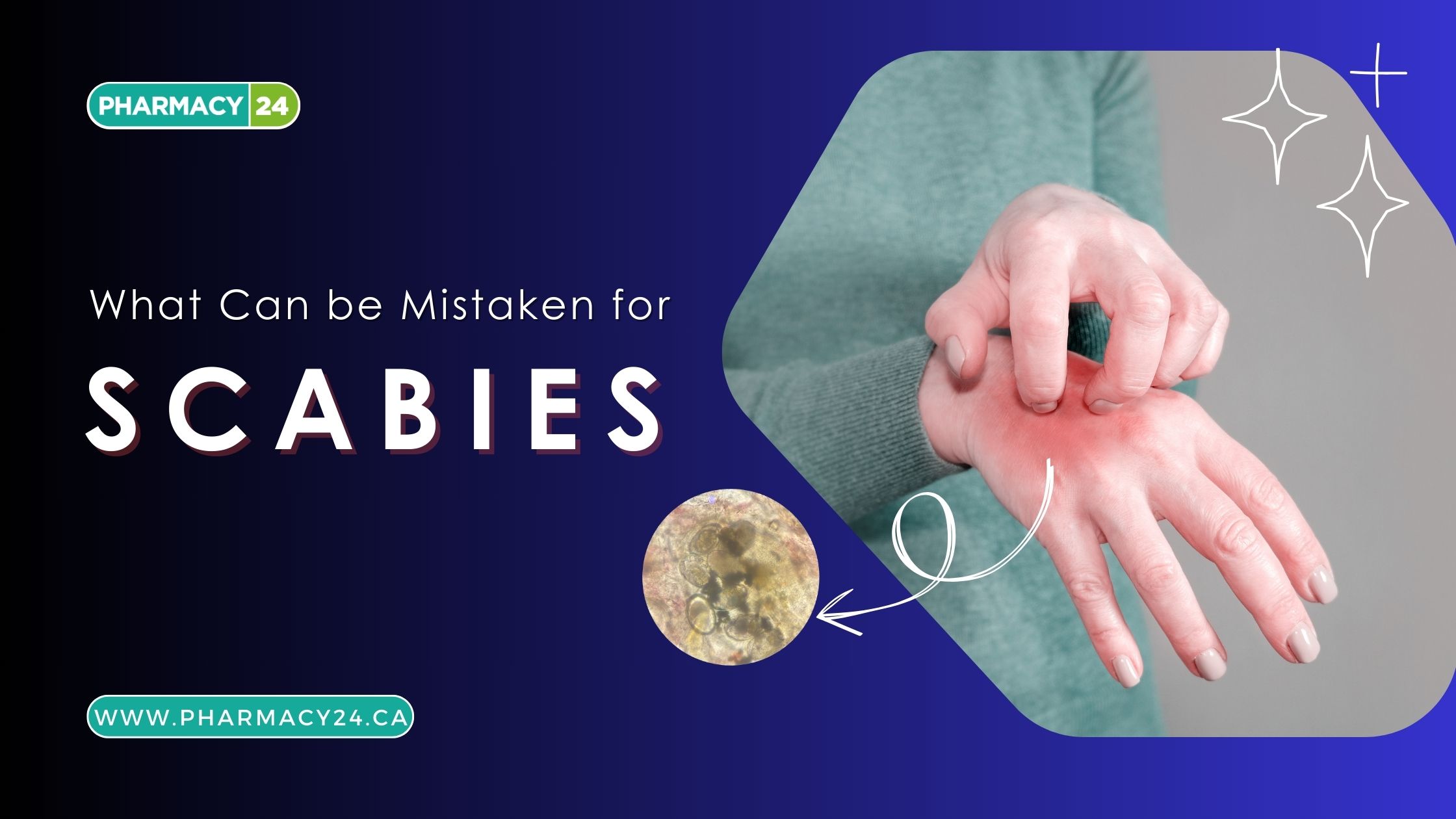
Have you noticed persistent itching or unusual skin rashes? While scabies is a common diagnosis, it’s not always the correct one.
Surprisingly, many other skin conditions share similar symptoms, leading to confusion and unnecessary treatments. Identifying the right condition is essential to getting effective relief.
This comprehensive guide “What Can be mistaken for scabies” aims to delineate these conditions, aiding in better understanding and accurate identification.
Buy The Best Product for Scabies – Nix Dermal Cream 30g [Permethrin 5%]
Key Takeaways
- Several skin conditions like Psoriasis, Atopic Dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis, Papular Urticaria, and Folliculitis are often mistaken for scabies due to similar symptoms.
- Accurate diagnosis is imperative for appropriate treatment and management.
- Awareness about these conditions and understanding their distinguishing features can aid in early and accurate diagnosis.
Conditions Mistaken for Scabies
[ux_image id=”26251″ height=”40%”]
[gap]
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red patches covered with silvery scales.
The resemblance in skin manifestations often leads to confusion between Psoriasis and Scabies.
Symptoms: Thick, scaly patches of skin, usually on the scalp, elbows, and knees. Itching may vary from mild to severe.
However, a closer inspection reveals distinct differences:
Origin: Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition, while scabies is an infestation.
Appearance: Psoriasis patches are thicker and may have silvery scales, unlike the more uniform, pimple-like rash of scabies.
Itching: Though both conditions cause itching, scabies tend to be more intense, especially at night.
Here’s a table summarizing the differences:
| Feature | Psoriasis | Scabies |
| Origin | Autoimmune | Infestation |
| Appearance | Red patches with silvery scales |
Pimple-like rash
|
| Itching | Yes |
More intense at night
|
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Atopic Dermatitis (AD), also known as eczema, exhibits symptoms like dry, itchy, and red skin, which are similar to scabies.
The differences include:
Duration: AD often has a chronic course, while scabies persist until treated.
Distribution: AD commonly affects the face, hands, and creases of the elbows or knees, unlike scabies, which often start between the fingers.
Medical News Today provides an in-depth comparison between Atopic Dermatitis and Scabies, enlightening the readers about their distinct features and manifestations.
Buy The Best Product for Scabies – Nix Dermal Cream 30g [Permethrin 5%]
Contact Dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis arises from skin contact with an allergen or irritant, causing a rash, itching, and sometimes blisters, akin to scabies symptoms.
Notable differences include:
Cause: Contact with allergens or irritants causes Contact Dermatitis, while scabies is due to mite infestation.
Area Affected: The rash in Contact Dermatitis is usually confined to the area of contact, unlike scabies, which can spread to other parts of the body over time.
Papular Urticaria
Papular Urticaria occurs due to insect bites, leading to an itchy rash similar to scabies.
Distinguishing factors are:
Cause: Insect bites cause Papular Urticaria, while a mite infestation causes scabies.
Appearance: Papular Urticaria often has a central punctum marking the bite site, which is not a feature of scabies.
Relevant information regarding Papular Urticaria and its differentiation from scabies can be found on Credihealth.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis, the inflammation of hair follicles, can also be mistaken for scabies due to its itchy, pustule-like lesions. However:
Affected Area: Folliculitis affects hair follicles, while scabies often start between the fingers and can spread to other body parts.
Diagnosis and Consultation
Accurate diagnosis of scabies or any other resembling condition is crucial for effective treatment.
It involves a thorough examination, often followed by a skin scraping test to identify the presence of mites or their eggs.
Seeking medical consultation is imperative to avoid misdiagnosis and receive appropriate treatment.
Scabies vs. Other Common Skin Conditions Table
| Condition | Key Symptoms | Cause | How It Differs from Scabies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scabies | Intense itching (worse at night), burrow-like lines, red bumps, and rashes. | Mite infestation | Involves burrows under the skin and spreads through prolonged contact. |
| Eczema | Dry, inflamed patches of skin, itching, and redness. | Overactive immune response | No burrows; often triggered by allergens or weather changes. |
| Psoriasis | Thick, scaly patches, often silvery, with mild to severe itching. | Immune system disorder | Silvery plaques are a hallmark; does not involve mites or burrowing. |
| Contact Dermatitis | A red, itchy rash that appears after exposure to an irritant or allergen. | Irritant exposure | Develops quickly after contact; no burrowing or nighttime itching. |
| Hives (Urticaria) | Raised, itchy welts that move around and disappear within hours or days. | Allergens or stress | Temporary condition; does not persist like scabies unless allergen exposure continues. |
| Fungal Infections | Circular, red patches with a clear center, often itchy. | Fungal organism | No burrowing or mites; often found in damp areas like feet or groin. |
| Bed Bug Bites | Small, red bumps in clusters, often on exposed areas of the skin. | Bed bug infestation | No burrows; bites are in linear or cluster patterns and limited to areas not covered by clothing. |
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing scabies and other similar conditions involves maintaining good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and seeking early medical intervention.
Depending on the diagnosed condition, treatment options may vary from topical creams to oral medications.
| Condition | Prevention | Treatment |
| Scabies | Good hygiene, Avoid contact with infected individuals |
Permethrin cream, Ivermectin
|
| Psoriasis | Stress management, Moisturizing |
Topical steroids, Light therapy
|
| Contact Dermatitis | Avoid allergens and irritants |
Topical steroids, Antihistamines
|
Buy The Best Product for Scabies – Nix Dermal Cream 30g [Permethrin 5%]
If you believe you may have scabies and want to know how to address it effectively, check out our guide on How to Get Rid of Scabies in 24 Hours for detailed treatment options and fast relief tips.”
Other Conditions Resembling Scabies
Scabies often get confused with other skin conditions due to the similarity in the appearance of rashes.
Some other conditions mistaken for scabies include acne and mosquito bites.
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition, especially among teenagers, characterized by pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads.
Unlike scabies, it’s primarily facial and tends to occur in areas with a high concentration of oil glands.
Appearance: Acne lesions are usually larger and less uniform than the rash caused by scabies.
Itching: Acne is less likely to cause itching compared to scabies.
Mosquito Bites
Mosquito bites can cause small, itchy bumps, somewhat resembling scabies.
Duration: The itching from mosquito bites tends to subside much quicker than scabies.
Spread: Unlike scabies, mosquito bites don’t spread through person-to-person contact.
Understanding the differences between these conditions and scabies is crucial to avoid misdiagnosis and ensure appropriate treatment. Detailed comparisons can be found on WebMD.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Psoriasis be mistaken for Scabies?
Yes, psoriasis can often be mistaken for scabies due to the appearance of rashes. However, unlike scabies, psoriasis patches are thicker and may have silvery scales.
What are the key differences between Contact Dermatitis and Scabies?
Contact Dermatitis arises from skin contact with an allergen or irritant, while scabies are due to mite infestation. The rash in Contact Dermatitis is usually confined to the area of contact, unlike scabies.
How can one differentiate between Papular Urticaria and Scabies?
Papular Urticaria often has a central punctum marking the bite site, which is not a feature of scabies. Moreover, the cause of Papular Urticaria is insect bites, while a mite infestation causes scabies.
Which medical tests are reliable for diagnosing Scabies?
A skin scraping test is commonly used to diagnose scabies by identifying the presence of mites or their eggs.
Is immediate medical consultation necessary for suspected Scabies?
Yes, seeking medical consultation is imperative to avoid misdiagnosis and receive appropriate treatment.
How long does it take for scabies cream to work?
Nix dermal cream, a commonly used scabies treatment, typically requires one application and should be left on the skin for at least 8 to 14 hours.
In some cases, a second application may be needed.
The treatment is designed to kill both the mites and their eggs, but itching may persist for several weeks due to the body’s allergic reaction to the mites and their feces.
If itching continues for more than 2 to 4 weeks after treatment, or if new burrows or rash lesions appear, retreatment may be necessary. [Source]
Conclusion
Understanding the nuanced differences between scabies and other resembling conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
This comprehensive exploration of “what can be mistaken for scabies” aims to aid in distinguishing scabies from other skin conditions, fostering better awareness and timely medical intervention.